| Sep 11, 2023 |
Setimane, V.; Sitiven, X.; Campira, N., Jessinau, S., Tome. A.; Tsamba , A.; Benjemane, F. [VS006] Mozambique |
|
K009001537 |
|
No
|
| Mar 29, 2016 |
Andru, J. [3301] Senegal |
|
K001105810 |
|
Yes
|
| Jan 1, 2009 |
Gossweiler, J. [4932] Angola |
|
K001276761 |
|
Yes
|
| Jan 1, 2009 |
Gossweiler, J. [3624] Angola |
|
K001276763 |
|
Yes
|
| Jan 1, 2009 |
Gossweiler, J. [11031] Angola |
|
K001276764 |
|
Yes
|
| Jan 1, 2009 |
Yeates, M. [88/Mali/2] Mali |
|
K000635110 |
|
Yes
|
| Jan 1, 2009 |
Gossweiler, J. [1719] Angola |
|
K001276762 |
|
Yes
|
|
Dalziel, J.M. [53] Nigeria |
|
K003183463 |
|
Yes
|
|
Schweinfurth, G. [890] Sudan |
|
K003183472 |
|
No
|
|
Dalziel, J.M. [314] Nigeria |
|
K003183466 |
|
Yes
|
|
Chapman, J.D. [4080] Nigeria |
|
K003183465 |
|
Yes
|
|
Bent, J.T. [s.n.] Sudan |
|
K003183476 |
|
No
|
|
Reekmans, M. [6345] Burundi |
|
K003183471 |
|
Yes
|
|
Charter, J.R. [FHI36998] Nigeria |
|
K003183449 |
|
Yes
|
|
[Murill] [L/4] Sudan |
|
K003183473 |
|
No
|
|
Dalziel, J.M. [314] Nigeria |
|
K003183468 |
|
Yes
|
|
Wickens, G.E. [2840] Sudan |
|
K003183494 |
|
No
|
|
Leeuwenberg, A.J.M. [7499] Cameroon |
|
K003183469 |
|
Yes
|
|
Dalziel, J.M. [314] Nigeria |
|
K003183451 |
|
Yes
|
|
s.coll. [25] Sudan |
|
K003183481 |
|
No
|
|
Meikle, R.D. [1214] Nigeria |
|
K003183467 |
|
Yes
|
|
Dudgeon, G.C. [4] Nigeria |
|
K003183462 |
|
Yes
|
|
Tuley, P. [2311] Nigeria |
|
K003183452 |
|
Yes
|
|
Cooke, B.K.; Adarashia, K. [115] Sudan |
|
K003183483 |
|
No
|
|
de Wilde, W.J.J.O.; de Wilde-Duyfjes, B.E.E.; de Wilde, W. [11031] Ethiopia |
|
K003183499 |
|
No
|
|
Harrison, M.N. [149] Sudan |
|
K003183480 |
|
No
|
|
Ehrenberg, C.G. [s.n.] Sudan |
|
K003183479 |
|
No
|
|
[illegible] [4658] Ghana |
|
K003183455 |
|
Yes
|
|
Elliott, W.R. [142] Nigeria |
|
K003183461 |
|
Yes
|
|
Speke (Capt.); Grant [771] Sudan |
|
K003183478 |
|
No
|
|
Wickens, G.E. [2882] Sudan |
|
K003183477 |
|
No
|
|
Wickens, G.E. [1496] Sudan |
|
K003183492 |
|
No
|
|
Tuley, P. [2312] Nigeria |
|
K003183448 |
|
Yes
|
|
Gillett, J.B. [4839] |
|
K003183498 |
|
No
|
|
Wickens, G.E. [2841] Sudan |
|
K003183496 |
|
No
|
|
Wickens, G.E. [2842] Sudan |
|
K003183490 |
|
No
|
|
Briston, S.C. [28] Sudan |
|
K003183493 |
|
No
|
|
Newby, J.E. [2P31] Niger |
|
K003183460 |
|
Yes
|
|
Schweinfurth, G. [747] Sudan |
|
K003183475 |
|
No
|
|
Bradley, P.N. [40] Niger |
|
K003183459 |
|
Yes
|
|
Okeke; Latilo; Odewo [FHI69303] Nigeria |
|
K003183464 |
|
Yes
|
|
Kitson, A. [713] Ghana |
|
K003183454 |
|
Yes
|
|
Wickens, G.E. [2920] Sudan |
|
K003183489 |
|
No
|
|
Alymer, G. [88] Sudan |
|
K003183482 |
|
No
|
|
Alymer, G. [87] Sudan |
|
K003183486 |
|
No
|
|
[Murill] [L/88] Sudan |
|
K003183474 |
|
No
|
|
Wickens, G.E. [2841] Sudan |
|
K003183497 |
|
No
|
|
Okeke; Latilo; Odewo [FHI69301] Nigeria |
|
K003183450 |
|
Yes
|
|
Wickens, G.E. [1284] Sudan |
|
K003183491 |
|
No
|
|
Francis, D. [52] Sudan |
|
K003183487 |
|
No
|
|
Rose Innes, R. [s.n.] Ghana |
|
K003183456 |
|
Yes
|
|
Robertson, V.C. [135] Sudan |
|
K003183484 |
|
No
|
|
Reinbold [Badra] [108] Niger |
|
K003183458 |
|
Yes
|
|
Wickens, G.E. [2843] Sudan |
|
K003183495 |
|
No
|
|
Wickens, G.E. [1573] Sudan |
|
K003183485 |
|
No
|
|
Ern, H. [3060] Togo |
|
K003183457 |
|
Yes
|
|
Sahni, K.C. [5] Sudan |
|
K003183488 |
|
No
|
|
Hepper, F.N. [3989] Cameroon |
|
K003183470 |
|
Yes
|
|
s.coll. [13] Nigeria |
|
K003183453 |
|
Yes
|
| Jan 1, 1963 |
Leeuwenberg, A.J.M. [4383] Burkina Faso |
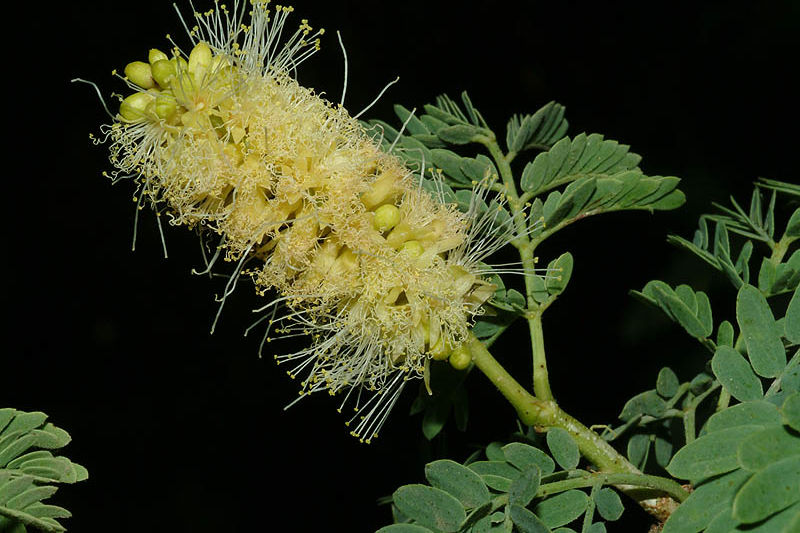
Acacia albida |
K000386659 |
|
Yes
|
|
Ward [65] Senegal |
Acacia albida |
K000232665 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Dubois, R. [213] Mali |
Acacia albida |
K000386660 |
|
Yes
|
|
Brunner [72] Senegal |
Acacia albida |
K000232648 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Schimper [33] Ethiopia |
Acacia albida |
K000244213 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Pfund, J. [17] Sudan |
Acacia albida |
K000244208 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Schimper [1333] Ethiopia |
Acacia albida |
K000244212 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Pfund, J. [87] Sudan |
Acacia albida |
K000244209 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Sieber [45] Senegal |
Acacia albida |
K000232646 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Sieber [45] Senegal |
Acacia albida |
K000232647 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Schweinfurth, G. [534] Sudan |
Acacia albida |
K000244210 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Heudelot [391] Senegal |
Acacia albida |
K000232651 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Wild, H. [2488] Zimbabwe |
Acacia albida |
K000244321 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Montbret [391] Senegal |
Acacia albida |
K000232649 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Robert [s.n.] Senegal |
Acacia albida |
K000232650 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|
|
Schweinfurth, G. [623] Sudan |
Acacia albida |
K000244211 |
Unknown Type Material |
Yes
|